Training your dog should be one of the most joyful and stress-free parts of your day. Each little two-minute session should be fast, fun, and something you look forward to. Here are three ideas to make getting to the fun part a little easier and for you to streamline dog training.
Idea Number 1: Covered treat bowls
It’s easy to find inexpensive little bowls with lids. Make up a big batch of your dog’s favorite “trail mix” and distribute it among the bowls. Scatter them around the house so every room has a treat container. Customize your dog’s treat mixture to reflect their preferences and make the mix a combination of high, middle, and low-value treats. That way your dog never knows what’s coming, and always hopes it’s the favorite. Be sure that all the treats are shelf-stable and will not get moldy. Some ideas to include are: kibble, air-popped popcorn, freeze-dried chicken heart pieces, circular oat cereal pieces, anything that’s small, dry, and a favorite for your dog. A recent student of ours used woven-wheat cereal squares. Worked beautifully, because her dog is crazy about them.
Having the treats close by makes it convenient to reward your dog spontaneously, especially when you’re trying to build your dog’s vocabulary. Say you walk into a room and your dog is lying there, it’s the work of a moment to say “Good Down!” and hand your dog a treat. But if the bowl wasn’t there, you couldn’t do it. If you had to leave the room to get the reward, your dog would probably follow you and the moment is lost.
With rewards close at hand, it will also remind you to mark the good decisions your dog makes – even if you’re just hanging out together on the couch. If a TV doorbell rings and your dog perks up but doesn’t bark – that’s a good decision worth rewarding. If someone walks by your window with a dog and your dog watches silently, that’s worth marking.
One of the most basic tenets of dog training is “what gets rewarded, gets repeated.” Make it easy for yourself to reward good behavior so your dog’s scales tilt that way more often.
Idea Number 2: Keep a list of games

You have all kinds of training games you play with your dog. Some have the names we gave them, others you’ve adapted and have your own names for them. If there’s a specific place that you go to train, keep a list of all your games there. That way, when it’s time to train but you don’t know what to play, the “cheat sheet” is right there. An instant way to streamline dog training.
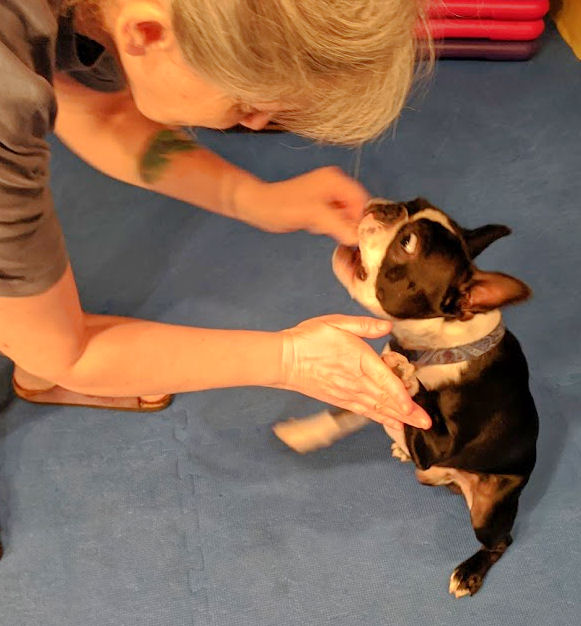
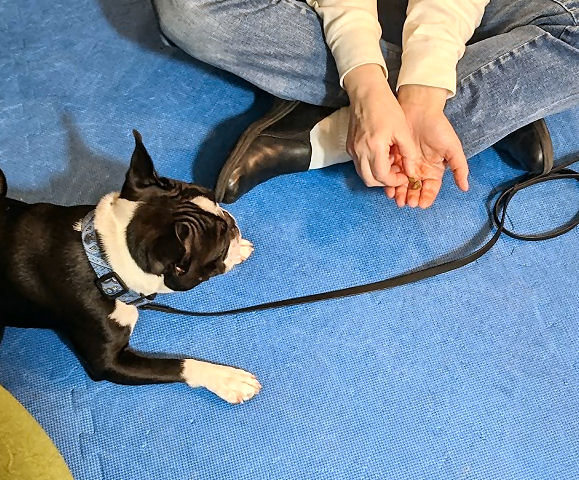
You can keep your list with your Session Log Book, even inside the front cover. We even try to jot down the date when we play a training game. We don’t want to go too long without playing certain skills games, like “Whatcha Gonna Do?” or “Looky-Loo.” Like any skill, training games can get rusty if they’re not used. (In the photo, Torque is doing “Gimme Your Face!“)
Idea Number 3: Keep a phone stand handy
Of all the training tools available to you – video is the most useful. You don’t have to share, or post, or even keep the videos you take of your training. But you should watch to get a different perspective on your training game sessions.
In addition to seeing (and hearing) all the times your timing was a bit off, or that you gave your dog the wrong direction, you’ll also see all the things you did right. It’s actually fun to go back and see how far you’ve come from where you and your dog started.
Another reason video is so valuable is that you can see and appreciate how smart, happy, and adorable your dog is. To actually see how your dog looks at you from a different perspective will make your heart swell. In a recent class, Fran took Booker for a spin through the Rally Obedience course and a student remarked on the lovely attention he paid to Fran throughout. The student didn’t even realize her dog’s gaze was almost identical when it was their turn.
We’re always open to new, fun, and functional hacks to make playing dog training games better and more fun. If you have a favorite trick you use to streamline dog training, please let us know!